Import Large SQL file Using MySQL command line
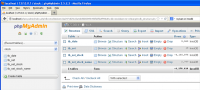
When you want to restore database from a SQL backup file to your MySQL server on web server, you can simply restore it using phpMyAdmin which is fast and easy.
However, if the backup file is a large SQL dump file, let’s say 50 MB, you can’t use phpMyAdmin because most server configuration haven’t been configured for large file uploading.
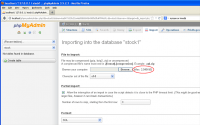
Solution
The best solution for import large SQL file to database is to use command line in MySQL. By importing database from command line, you won’t have to worry with any PHP restriction, such as, upload_max_filesize, post_max_size, maximum execution time, etc, which usually are limited to some value in PHP configuration.
To execute MySQL command line for import SQL file, the syntax is:
mysql -u user_name -p -h host_name database_name < dump_file.sql |
Where
- user_name is username to execute this import operation.
- host_name is target database hostname.
- database_name is target database name.
- dump_file.sql is SQL file.
Note: The syntax is the same for both Windows and Linux platforms.
Let’s see some example
mysql -u root -p -h localhost stock < stock.sql |
The above command will import database from a file “stock.sql” to the server “localhost” on database “stock” using user “root”. You will be asked to enter password for the user once you execute the command.
If there is any error occurs while importing, it will display on the screen.
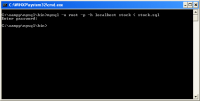
Once the importing process is finished without any error, you can use the data as you want.