- Accessing MariaDB on NetBeans 8.2 using JDBC, Part 1: Install Employees sample database and grant permission
- Accessing MariaDB on NetBeans 8.2 using JDBC, Part 2: Create a connection
- Accessing MariaDB on NetBeans 8.2 using JDBC, Part 3: Perform SQL Operations
From Part 2, I have established a connection to employees database on MariaDB. Now, I’ll show how to retrieve and modify data from the database.
Retrieve data from a table
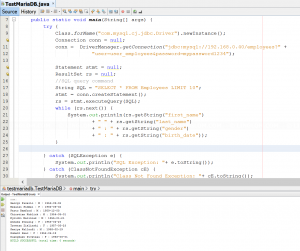
To get data, I send query to MariaDB server and get result back. First, I create stmt (Statement object) and execute SQL query. Then I store the result on ResultSet object and iterative show the result on output window.
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; //SQL query command String SQL = "SELECT * FROM Employees LIMIT 10"; stmt = conn.createStatement(); rs = stmt.executeQuery(SQL); while (rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("first_name") + " " + rs.getString("last_name") + " : " + rs.getString("gender") + " : " + rs.getString("birth_date")); } |
Code Explanation:
- Line 18: creates a Statement object for sending SQL queries to the database.
- Line 19: executes the SQL statement and returns a single ResultSet object
- Line 20-25, in while-loop, iterative in the ResultSet object to show result in console (first_name, last_name, gender, and birth_date columns in Employees table) on output window.
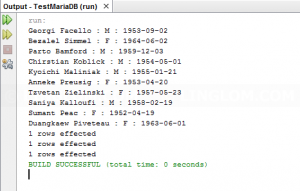
Sample result will be similar to the below figure.
Note: I have limit only first 10 records from the table.
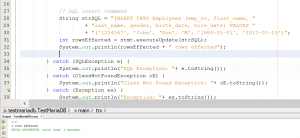
Insert record to a table
To insert a new record, you can use the code above and simply change SQL command, modify some code a little bit.
27 28 29 30 31 32 | // SQL insert command String strSQL = "INSERT INTO Employees (emp_no, first_name, " + "last_name, gender, birth_date, hire_date) VALUES " + "('1234567', 'John', 'Doe', 'M', '1980-01-01', '2017-01-10')"; int rowsEffected = stmt.executeUpdate(strSQL); System.out.println(rowsEffected + " rows effected"); |
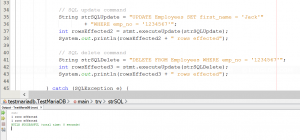
Update data on a table
Update and delete record code are the same with insert, only change in SQL statement.
34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | // SQL update command String strSQLUpdate = "UPDATE Employees SET first_name = 'Jack'" + "WHERE emp_no = '1234567'"; int rowsEffected2 = stmt.executeUpdate(strSQLUpdate); System.out.println(rowsEffected2 + " rows effected"); // SQL delete command String strSQLDelete = "DELETE FROM Employees WHERE emp_no = '1234567'"; int rowsEffected3 = stmt.executeUpdate(strSQLDelete); System.out.println(rowsEffected3 + " rows effected"); |
Summary
You can download source code example at TestMariaDB.java (right-click the link and select Save target As). But you have to change connection string to match your environment.
The example code will connect to Employess database and try to retrieve records, insert a new record, update the record and delete the record from Employees table. The result is below.
Thank you. This is what I like about the net – always someone to help out. Given time I would have worked this out myself but you have saved me many hours. CHEERS!